4 Common Misconceptions About CPR
Think you know CPR? Discover 4 common misconceptions that could impact life-saving efforts and learn the truth behind them.
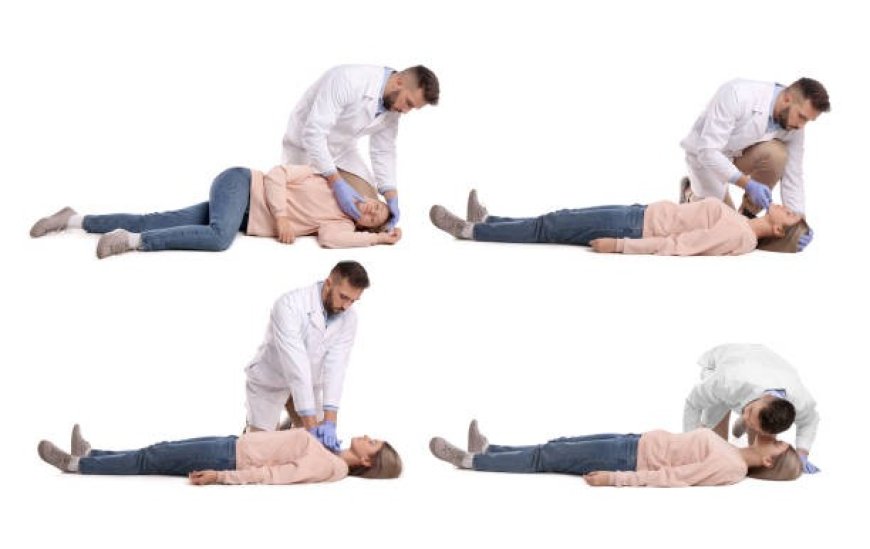
Performing immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) can help increase survival rates in the event of a medical emergency. Whether during a cardiac arrest or traumatic injuries, this procedure will help keep victims alive while awaiting professional assistance. Despite being a life-saving skill, some people hesitate to perform the procedure due to a mix of fear and misconceptions. Here are a few common misconceptions about cardiopulmonary resuscitation and why they shouldn’t stop you:
1. CPR Is for Professionals Only
This is the most common misconception that causes many people to hesitate when administering CPR. Emergencies, such as cardiac arrest, will often occur outside healthcare facilities. They may occur at home, on the streets, or at school, where medical professionals are not readily available. As a bystander, you don’t have to wait for professionals to come and perform this life-saving procedure.
If you’ve learned the basics of performing this procedure, you can attend to victims of medical emergencies and save lives. Administering cardiopulmonary resuscitation correctly doesn’t require years of medical training. A quality training program will teach you basic techniques, such as rescue breaths and chest compressions. When it comes to advanced training, you will learn how to utilize devices like automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
2. It’s Only for Cardiac Arrest Victims
Some people believe that this procedure is only necessary during cardiac arrest. Although cardiopulmonary resuscitation is commonly used for cardiac arrest, it’s also used during medical emergencies like drowning. The procedure can also help restore breathing in victims of electric shock. Perform this procedure when the victim is not breathing normally or is unresponsive. When performed immediately and correctly, the procedure will help sustain necessary organs, especially in cases involving drowning, suffocation, and substance overdose.
3. It Always Saves Lives
Although cardiopulmonary resuscitation is a life-saving procedure, it doesn’t assure survival. Individuals performing this procedure need to do it correctly to increase survival rates. The aim is to keep the victim’s blood and oxygen flowing to the organs until professional help arrives. According to the American Heart Association (AHA), cardiopulmonary resuscitation can double or triple an individual’s chance of surviving cardiac arrest. Survival chances decrease every minute this procedure is delayed. Other factors that may affect the outcome include the person’s overall health and the cause of cardiac arrest.
4. You Need Special Equipment
One of the main reasons why some people hesitate to start cardiopulmonary resuscitation is a lack of special equipment. They may believe that they need AEDs, face masks, or other medical equipment to start the procedure. Contrary to this belief, you don’t need special equipment to start this life-saving method. All you need to save a life are your hands, especially for cardiac arrest victims.
You can use the hands-only cardiopulmonary resuscitation method by providing continuous chest compressions. If the victim collapses and stops breathing, a rescue breath may help keep them alive until professional help arrives. This method requires pinching the victim’s nostrils shut and gently breathing into their mouth. Reputable CPR courses are taught by certified instructors and will provide you with the knowledge you need to perform CPR or mouth-to-mouth.
Learn How To Save Lives Today
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is a valuable skill that you can learn and use to save lives during medical emergencies. By debunking common misconceptions about the procedure, some individuals may be more encouraged to attempt this skill during an emergency. Proper training on how to perform CPR will help you act with confidence when attending to victims of cardiac arrest, choking, or substance abuse. You will learn how to provide chest compressions and utilize AEDs to increase survival rates. Learn how to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation today.







